
When Aaron Barr was finalizing a recent computer security presentation for the US Transportation Security Administration, a colleague had a bit of good-natured advice for him: "Scare the sh*t out of them!"
In retrospect, this may not have been the advice Barr needed. As CEO of the government-focused infosec company HBGary Federal, Barr had to bring in big clients—and quickly—as the startup business hemorrhaged cash. To do so, he had no problem with trying to "scare the sh*t out of them." When working with a major DC law firm in late 2010 on a potential deal involving social media, for instance, Barr decided that scraping Facebook to stalk a key partner and his family might be a good idea. When he sent his law firm contact a note filled with personal information about the partner, his wife, her family, and her photography business, the result was immediate.
"Thanks. I am not sure I will share what you sent last night—he might freak out."
This rather creepy behavior became common; Barr used it as a sign of his social media prowess. Another target of his investigations went to "a Jewish Church in DC, the Temple Micah." Someone else "married @ the Inn at Perry Cabin in St. Michaels, MD (non-denominational ceremony)." Barr was even willing to helpfully guesstimate the ages of children in photographs ("they have 2 kids, son and daughter look to be 7 and 4").

With one potential client, Barr sifted the man's social media data and then noted that "I am tempted to create a person from his highschool and send him a request, but that might be overstepping it."
As the money ran out on HBGary Federal, Barr increasingly had no problem "overstepping it." In November, when a major US bank wanted a strategy for taking down WikiLeaks, Barr immediately drafted a presentation in which he suggested "cyber attacks against the infrastructure to get data on document submitters. This would kill the project. Since the servers are now in Sweden and France, putting a team together to get access is more straightforward."
Faking documents seemed like a good idea, too, documents which could later be "called out" so as to make WikiLeaks look unreliable.
And Barr wanted to go further, pushing on people like civil liberties Salon.com columnist Glenn Greenwald—apparently hoping to threaten their livelihoods. "These are established professionals that have a liberal bent, but ultimately most of them if pushed will choose professional preservation over cause, such is the mentality of most business professionals," he wrote. "Without the support of people like Glenn WikiLeaks would fold."
When the US Chamber of Commerce wanted to look into some of its opponents, Barr teamed with two other security companies and went nuts, proposing that the Chamber create an absurdly expensive "fusion cell" of the kind "developed and utilized by Joint Special Operations Command (JSOC)"—and costing $2 million a month. And if the fusion cell couldn't turn up enough opposition research, the security firms would be happy to create honeypot websites to lure the Chamber's union-loving opponents in order to grab more data from them.
The security companies even began grabbing tweets from liberal activists and mapping the connections between people using advanced link analysis software most often used by the intelligence community. (Some of the Chamber material was unearthed by ThinkProgress and other liberal bloggers, while The Tech Herald and Crowdleaks.org first wrote about the proposed WikiLeaks attacks.)
While waiting to see if his proposals would result in work for HBGary Federal, Barr turned in January to unmask the leadership of the hacker collective Anonymous. This part of the story is well known by now (read our investigative feature): when Barr went public with his findings, Anonymous took down his website, stole his e-mails, deleted the company's backup data, trashed Barr's Twitter account, and remotely wiped his iPad.
In the days since the attack and the publication of Barr's e-mails, his partners at other security firms threw him under the bus. "I have directed the company to sever any and all contacts with HB Gary," said the CEO of Palantir.
Berico Technologies, another private security firm, said that it "does not condone or support any effort that proactively targets American firms, organizations or individuals. We find such actions reprehensible and are deeply committed to partnering with the best companies in our industry that share our core values. Therefore, we have discontinued all ties with HBGary Federal."
Glenn Greenwald unleashed both barrels of his own, claiming that "what is set forth in these proposal... quite possibly constitutes serious crimes. Manufacturing and submitting fake documents with the intent they be published likely constitutes forgery and fraud. Threatening the careers of journalists and activists in order to force them to be silent is possibly extortion and, depending on the specific means to be used, constitutes other crimes as well. Attacking WikiLeaks' computer infrastructure in an attempt to compromise their sources undoubtedly violates numerous cyber laws."
How did Barr, a man with long experience in security and intelligence, come to spend his days as a CEO e-stalking clients and their wives on Facebook? Why did he start performing "reconnaissance" on the largest nuclear power company in the US? Why did he suggest pressuring corporate critics to shut up, even as he privately insisted that corporations "suck the lifeblood out of humanity"? And why did he launch his ill-fated investigation into Anonymous, one which may well have destroyed his company and damaged his career?
Thanks to his leaked e-mails, the downward spiral is easy enough to retrace. Barr was under tremendous pressure to bring in cash, pressure which began on November 23, 2009.
"A" players attract "A" players
That's when Barr started the CEO job at HBGary Federal. Its parent company, the security firm HBGary, wanted a separate firm to handle government work and the clearances that went with it, and Barr was brought in from Northrup Grumman to launch the operation.
In an e-mail announcing Barr's move, HBGary CEO Greg Hoglund told his company that "these two are A+ players in the DoD contracting space and are able to 'walk the halls' in customer spaces. Some very big players made offers to Ted and Aaron last week, and instead they chose HBGary. This reflects extremely well on our company. 'A' players attract 'A' players."
Barr at first loved the job. In December, he sent an e-mail at 1:30am; it was the "3rd night in a row I have woken up in the middle of the night and can't sleep because my mind is racing. It's nice to be excited about work, but I need some sleep."
Barr had a huge list of contacts, but turning those contacts into contracts for government work with a fledgling company proved challenging. Less than a year into the job, HBGary Federal looked like it might go bust.
On October 3, 2010, HBGary CEO Greg Hoglund told Aaron that "we should have a pow-wow about the future of HBGary Federal. [HBGary President] Penny and I both agree that it hasn't really been a success... You guys are basically out of money and none of the work you had planned has come in."
Aaron agreed. "This has not worked out as any of us have planned to date and we are nearly out of money," he said.
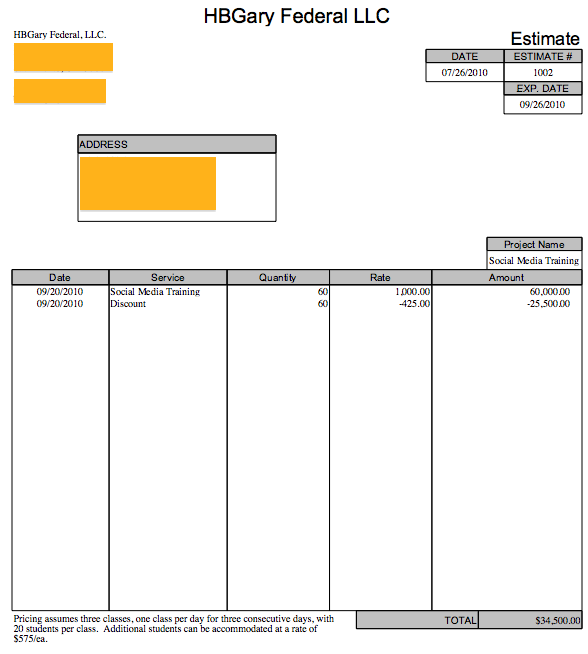
While he worked on government contracts, Barr drummed up a little business doing social media training for corporations using, in one of his slides, a bit of research into one Steven Paul Jobs.
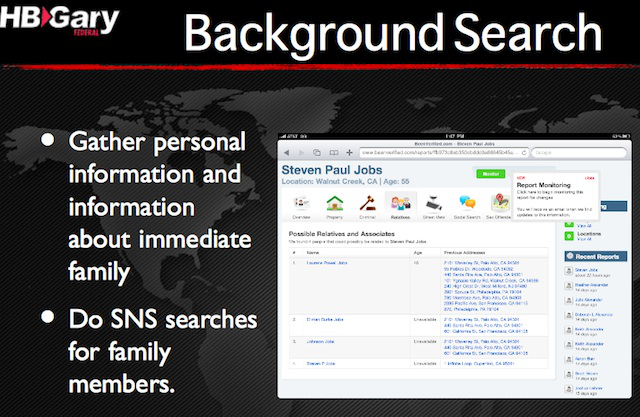
The training sessions, following the old "scare the sh*t out of them" approach, showed people just how simple it was to dredge up personal information by correlating data from Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, and more. At $1,000 per person, the training could pull in tens of thousands of dollars a day, but it was sporadic. More was needed; contracts were needed, preferably multi-year ones.
The parent company also had issues. A few weeks after the discussions about closing up HBGary Federal, HBGary President Penny Leavy-Hoglund (Greg's wife), sent an e-mail to her sales team, telling them "to work a quota and to bring in revenue in a timely manner. It's not 'optional' as to when it needs to close, if you haven't met your number, the closing needs to happen now, not later. You need to live, eat, breath and ensure you meet your number, not kind of hit it, MEET IT... Guys, no one is making their quota."
She concluded darkly, "I have some serious doubts about some people's ability to do their job. There will be changes coming shortly and those decisions will be new people's to make."
And then, unexpectedly, came the hope of salvation.
reader comments
188