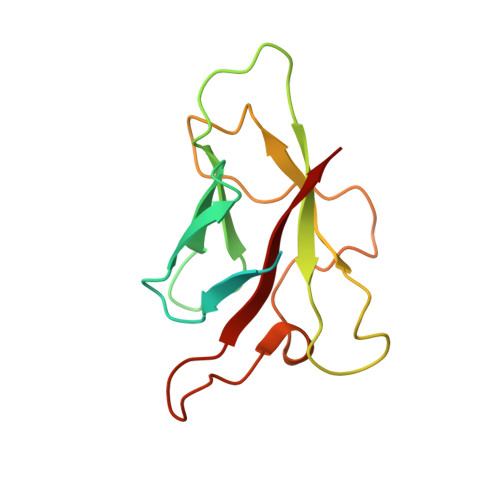
Crystal structures of flax rust avirulence proteins AvrL567-A and -D reveal details of the structural basis for flax disease resistance specificity.
Wang, C.I., Guncar, G., Forwood, J.K., Teh, T., Catanzariti, A.M., Lawrence, G.J., Loughlin, F.E., Mackay, J.P., Schirra, H.J., Anderson, P.A., Ellis, J.G., Dodds, P.N., Kobe, B.(2007) Plant Cell 19: 2898-2912
- PubMed: 17873095
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.053611
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2QVT - PubMed Abstract:
The gene-for-gene mechanism of plant disease resistance involves direct or indirect recognition of pathogen avirulence (Avr) proteins by plant resistance (R) proteins. Flax rust (Melampsora lini) AvrL567 avirulence proteins and the corresponding flax (Linum usitatissimum) L5, L6, and L7 resistance proteins interact directly. We determined the three-dimensional structures of two members of the AvrL567 family, AvrL567-A and AvrL567-D, at 1.4- and 2.3-A resolution, respectively. The structures of both proteins are very similar and reveal a beta-sandwich fold with no close known structural homologs. The polymorphic residues in the AvrL567 family map to the surface of the protein, and polymorphisms in residues associated with recognition differences for the R proteins lead to significant changes in surface chemical properties. Analysis of single amino acid substitutions in AvrL567 proteins confirm the role of individual residues in conferring differences in recognition and suggest that the specificity results from the cumulative effects of multiple amino acid contacts. The structures also provide insights into possible pathogen-associated functions of AvrL567 proteins, with nucleic acid binding activity demonstrated in vitro. Our studies provide some of the first structural information on avirulence proteins that bind directly to the corresponding resistance proteins, allowing an examination of the molecular basis of the interaction with the resistance proteins as a step toward designing new resistance specificities.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Molecular and Microbial Sciences, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia.