Abstract
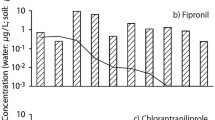
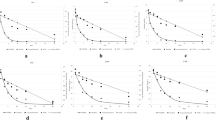
The effect of imidacloprid and fipronil on Sympetrum infuscatum larvae and adults during the rice cultivation period was monitored using an experimental micro-paddy lysimeter (MPL) system. Twenty-two hatched larvae were laid on the soil surface of each MPL. MPLs were treated with imidacloprid, fipronil, and the control MPL was left untreated. The pesticide concentration, S. infuscatum larval and adult populations, and larval emergence time were monitored in each MPL. The maximum imidacloprid and fipronil concentration in paddy water was 52.8 μg/l at 1 day, and 1.3 μg/l at 6 h, respectively, after the pesticide application. Both pesticides dissipated quickly in paddy water, with half-lives of 8.8 and 5.4 days for imidacloprid and fipronil, respectively. The absence of S. infuscatum larvae and exuviae in the fipronil-treated MPL was remarkable. The larval survival decreased to 63.6 ± 18.2, 15.2 ± 2.6, and 0% in the control, imidacloprid-treated, and fipronil-treated MPLs, respectively, by 9 days after pesticide application. Emergence in the imidacloprid-treated MPL was also significantly lower than that in the control MPL. The observed decrease in the abundances of S. infuscatum larvae and adults in MPLs seems to be both directly and indirectly associated with nursery-box application of fipronil and imidacloprid.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aajoud A, Ravanel P, Tissut M (2003) Fipronil metabolism and dissipation in a simplified aquatic ecosystem. J Agric Food Chem 51:1347–1352
Ali A, Chowdhury MA, Hossain MI, Ameen M-U, Habiba DB, Aslam AFM (1999) Laboratory evaluation of selected larvicides and insect growth regulators against field-collected Culex quinquefasciatus larvae from urban Dhaka, Bangladesh. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 15:43–47
Asaka S, Kawauchi N, Koyama S, Emura K (1978) Fate of propaphos (Kayaphos) applied on seedling box. J Pest Sci 3:305–310
Cohen JE et al (1994) A food-web approach to evaluating the effect of insecticide spraying on insect pest population-dynamics in a Philippine irrigated rice ecosystem. J Appl Ecol 31:747–763
Corbet PS (1999) Dragonflies: behavior and ecology of Odonata. Cornell University Press, Ithaca
Fossen M (2006) Environmental fate of imidacloprid. In: environmental monitoring, Department of Pesticide Regulation, California, pp 1–16
Gunasekara AS, Truong T, Goh KS, Spurlock F, Tjeerdema RS (2007) Environmental fate and toxicology of fipronil. J Pest Sci 32:189–199
Han M-S et al (2010) Aquatic invertebrate in paddy ecosystem of Korea. Kwang Monn Dang Press, Suwon
Iwaya K, Kagabu S (1998) Biological properties of the chloronicotinyl insecticide imidacloprid: high selectivity and safer use in practice. Rev Toxicol 2:121–132
Jinguji H, Tsuyuzaki H (2008) Stadium construction and development of Sympetrum frequens (Selys), S. darwinianum (Selys) and S. infuscatum (Selys) larva. Tombo, Matsumoto 51:38–42 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Jinguji H, Uéda T, Goka K, Hidaka K, Matsura T (2009) Effects of imidacroprid and fipronil insecticide application on the larvae and adults of Sympetrum frequens. JSIDRE 259:355–360 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Jinguji H, Tuyuzaki H, Uéda T (2010) Effects of temperature and light on the hatching of overwintering eggs in three Japanese Sympetrum species. Paddy Water Environ 8:385–391
Liu WP, Zheng W, Gan JY (2002) Competitive sorption between imidacloprid and imidacloprid-urea on soil clay minerals and humic acids. J Agric Food Chem 50:6823–6827
Matson PA, Parton WJ, Power AG, Swift MJ (1997) Agricultural intensification and ecosystem properties. Science 277:504–509
Nakano S, Asahina S, Miura T (1977) The paddy field Odonata collected in Thailand, the Philippines and Hong Kong. Bulletin of the Institute of Tropical Agriculture, Kyushu University, Fukuoka 2:172–186
Nhung DT, Phong TK, Watanabe H, Iwafune T, Thuyet DQ (2009) Simulating the dissipation of two herbicides using micro paddy lysimeters. Chemosphere 77:1393–1399
Overmyer JP, Mason BN, Armbrust KL (2005) Acute toxicity of imidacloprid and fipronil to a nontarget aquatic insect, Simulium vittatum Zetterstedt cytospecies IS-7. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 74:872–879
Phong TK, Nhung DT, Motobayashi T, Thuyet DQ, Watanabe H (2009) Fate and transport of nursery-box-applied tricyclazole and imidacloprid in paddy fields. Water Air Soil Pollut 202:3–12
Sanchez-Bayo F, Goka K (2006a) Ecological effects of the insecticide imidacloprid and a pollutant from antidandruff shampoo in experimental rice fields. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:1677–1687
Sanchez-Bayo F, Goka K (2006b) Influence of light in acute toxicity bioassays of imidacloprid and zinc pyrithione to zooplankton crustaceans. Aquat Toxicol 78:262–271
Schoenly KG, Justo HD, Barrion AT, Harris MK, Bottrell DG (1998) Analysis of invertebrate biodiversity in a Philippine farmer’s irrigated rice field. Environ Entomol 27:1125–1136
Settle WH et al (1996) Managing tropical rice pests through conservation of generalist natural enemies and alternative prey. Ecology 77:1975–1988
Song MY, Stark JD, Brown JJ (1997) Comparative toxicity of four insecticides, including imidacloprid and tebufenozide, to four aquatic arthropods. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:2494–2500
Stevens MM, Helliwell S, Warren GN (1998) Fipronil seed treatments for the control of chironomid larvae (Diptera : Chironomidae) in aerially-sown rice crops. Field Crop Res 57:195–207
Stoughton SJ, Liber K, Culp J, Cessna A (2008) Acute and chronic toxicity of imidacloprid to the aquatic invertebrates Chironomus tentans and Hyalella azteca under constant- and pulse-exposure conditions. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:662–673
Sugimura M, Ishida S, Kojima K, Ishida K, Aoki H (1999) Dragonflies of the Japanese archipelago in color. Hokkaido University Press, Sapporo
Swift MJ, Anderson JM (1994) Biodiversity and ecosystem function in agricultural systems. In: Schulze ED, Mooney HA (eds) Biodiversity and ecosystem function. Springer, Berlin, pp 15–41
Thuyet DQ, Hien TQ, Watanabe H, Saito H, Phong TK, Nishimura T (2010a) Micro paddy lysimeter for monitoring solute transport in paddy environment. Paddy Water Environ 8:235–245
Thuyet DQ, Ok J, Thuy DQ, Motobayashi T, Watanabe H (2010b) Effect of treatment methods of nursery boxes applied insecticide on the behavior of fipronil in rice paddy field. In: Proceedings of the 11th international symposium for environmental issues in Korea and Japan, KyungHee University, Yongin-Si, Korea, pp 92–98
Thuyet DQ, Watanabe H, Yamazaki K, Takagi K (2011a) Photodegradation of imidacloprid and fipronil in rice–paddy water. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:548–553
Thuyet DQ, Watanabe H, Motobayashi T (2011b) Effect of formulations and treatment methods of nursery boxes applied with insecticide on the behavior of imidacloprid in rice paddy fields. J Pest Sci 36:9–15
Thuyet DQ, Watanabe H, Takagi K, Yamazaki K, Nhung DT (2012) Behavior of nursery-box-applied imidacloprid in micro paddy lysimeter. J Pest Sci 37(1):20–27
Uéda T (2008a) A recent striking tendency to decrease in Sympetrum frequens and the estimated year when it started-from the survey using questionnaires to the members of Aka-tombo network. Symnet 10:6–7 (in Japanese)
Uéda T (2008b) The results of 2007 Sympetrum censuses at various localities in Japan by the members of Aka-tombo network (prompt report). Symnet 10:8–10 (in Japanese)
Watanabe M, Matsuoka H, Susa K, Taguchi M (2005) Thoracic temperature in Sympetrum infuscatum (Selys) in relation to habitat and activity (Anisoptera : Libellulidae). Odonatologica 34:271–283
Way MJ, Heong KL (1994) The role of biodiversity in the dynamics and management of insect pests of tropical irrigated rice—a review. Bull Entomol Res 84:567–587
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Kyoko Jinguji and Mitsuo Saito for assistance with MPL experiments. This study was supported primarily by a Grant-in-Aid for Biological Studies on Wildlife under the Framework ExTEND2005, and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (22580278) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jinguji, H., Thuyet, D.Q., Uéda, T. et al. Effect of imidacloprid and fipronil pesticide application on Sympetrum infuscatum (Libellulidae: Odonata) larvae and adults. Paddy Water Environ 11, 277–284 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-012-0317-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-012-0317-3